EGS5での計算結果です。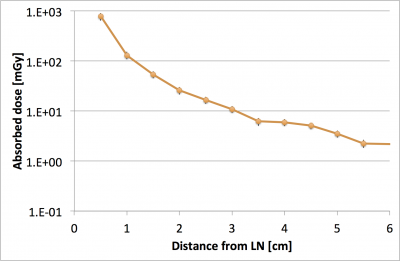
米国FDAから承認が得られた薬剤例
https://www.fda.gov/forconsumers/byaudience/forwomen/ucm118628.htm
妊娠と放射線診療
ICRP 84, Pregnancy and medical radiation (1.3 Mb)
関連した検討例
鍵野友美, 福嶋豊, 飯田英博, 近野勝正, 高田政彦.手術時に発生する血液による放射性汚染物の取扱方法の検討
センチネルリンパ節生検 : 術中迅速組織診断の被曝量は安全か?
渡辺 浩.センチネルリンパ節生検の実際】従事者の被曝線量とその理解の仕方
Aalbersberg EA, Verwoerd D, Mylvaganan-Young C, de Barros HA, van Leeuwen PJ, Sonneborn-Bols M, Donswijk ML. Occupational Radiation Exposure of Radiopharmacy, Nuclear Medicine, and Surgical Personnel During Use of [99mTc]Tc-PSMA-I&S for Prostate Cancer Surgery. J Nucl Med Technol. 2021 Dec;49(4):334-338. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.121.262161. Epub 2021 Jul 30. PMID: 34330802.
沼田奈々, 大川千絵, 伊藤理恵子, 阿部佳代子, 中英男. センチネルリンパ節生検 : 術中迅速組織診断の被曝量は安全か? 医学検査 : 日本臨床衛生検査技師会誌. 2004;53:969–72.
IAEA No. SSG-46
There may be situations with high doses, for example in medical emergencies involving immediate care of patients in the case of a stroke or cardiac arrest, when large amounts of radioactive material have been incorporated (e.g. 2 GBq of 131I), but in these events the dose is justified because the procedure is lifesaving. However, even in the case of urgent surgery, rotation of personnel may be utilized if the surgical procedure is lengthy to help to maintain optimized occupational radiation protection for this situation. The advice of the facility’s RPO should be sought for these situations (see the guidance in paras 4.299 and 4.300 for more details).